Navigating the maze of APIs, SDKs, and PCI compliance can make figuring out how to integrate payment gateway in mobile app feel like a high-stakes challenge. Choosing the wrong provider leads to security vulnerabilities, opaque fee structures, and a clunky user experience that kills conversions. For many developers, this critical step becomes a significant bottleneck, delaying launch and introducing unnecessary risk.
This definitive guide eliminates that complexity. We provide a clear, actionable roadmap that cuts through the noise. We’ll walk you through the complete, step-by-step process—from evaluating the best gateways and their costs to implementing a rock-solid integration using the right tools. You will gain the technical clarity and confidence to build a seamless, enterprise-grade payment system that delights your users and protects your business, turning a daunting task into a powerful asset.
Pre-Integration Essentials: Planning Your Mobile Payment Strategy
Before writing a single line of code, a robust strategy is essential for a successful payment integration. The first step is to define your app’s monetization model. Are you processing one-time payments for physical goods, managing recurring subscriptions for a service, or enabling simple in-app purchases? This core decision directly impacts how to integrate payment gateway in mobile app and the specific features you will need from a provider.
For a high-level overview of the process, this video provides a helpful visual guide:
Next, you must understand the key players. The complex mobile payment ecosystem consists of three core components: the merchant account (where funds are held), the payment processor (who communicates with card networks), and the payment gateway (the secure go-between for your app and the processor). Modern gateways often bundle these services for simplicity. A successful integration is user-centric, so map the entire payment flow from cart to confirmation and identify your target audience’s preferred payment methods. Supporting credit cards is standard, but offering digital wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay is crucial for a frictionless checkout experience.
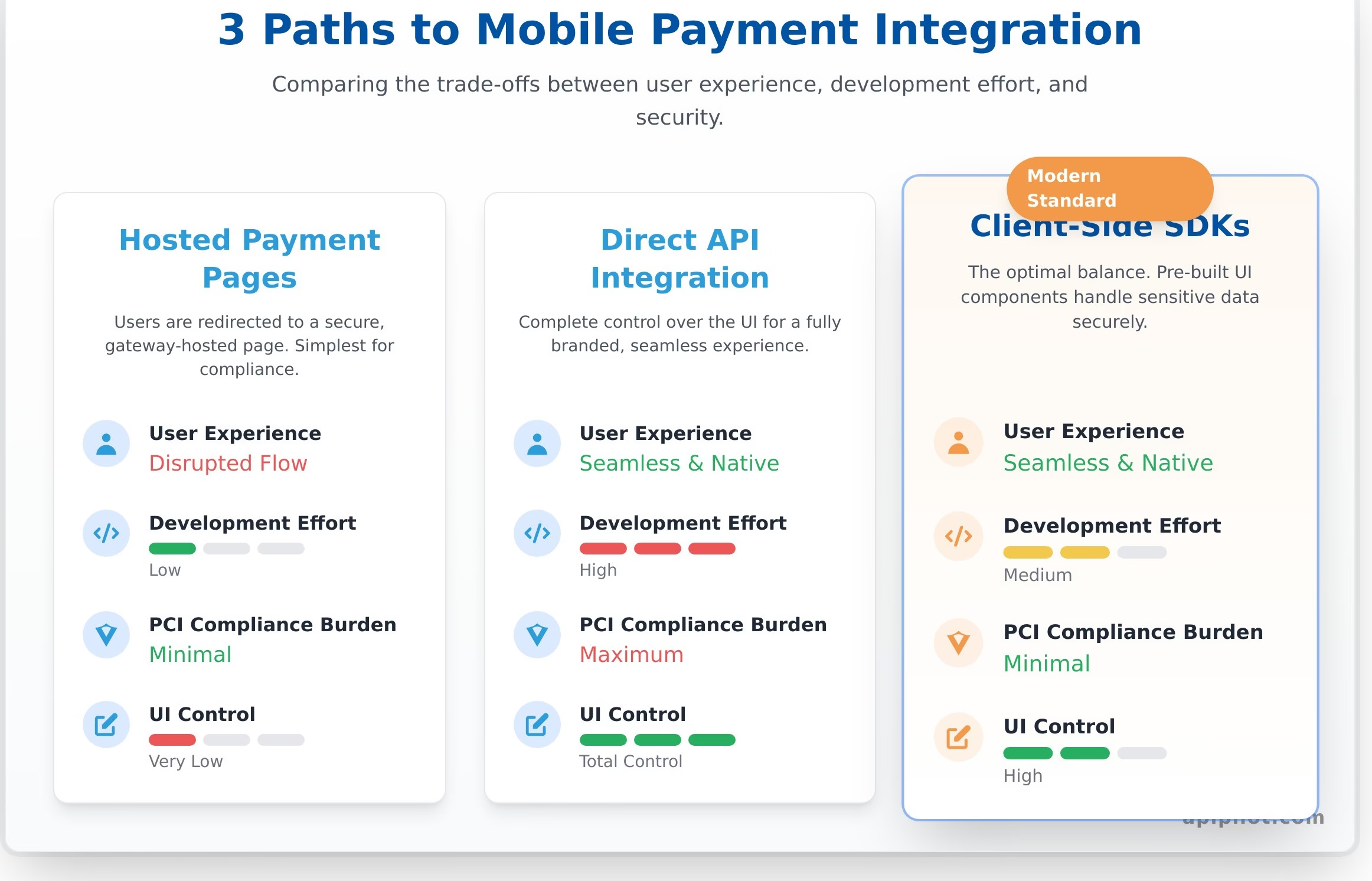
Choosing the Right Type of Integration
Your choice of integration method dictates the balance between user experience, development effort, and compliance overhead. There are three primary models to consider:
- Hosted Payment Pages: The simplest for compliance. Users are redirected to a secure page hosted by the gateway, but this can disrupt the native app feel.
- Direct API Integration: Offers complete control over the UI for a seamless, branded experience. However, it places the full PCI DSS compliance burden on your systems.
- Client-Side SDKs: The modern standard for native apps. SDKs provide pre-built UI components, simplifying development while handling sensitive data securely to strike an optimal balance.
Key Features to Look for in a Payment Gateway
When evaluating potential gateways, prioritize these enterprise-grade features to ensure a scalable and secure solution:
- Robust Security: The provider must handle PCI DSS compliance, tokenization, and fraud detection to protect you and your users.
- Multi-Currency & Payment Methods: Support for global currencies and popular payment methods like Apple Pay and Google Pay is critical for reaching a wider audience.
- Developer-First Tools: Clear documentation, powerful SDKs for iOS and Android, and a reliable sandbox environment are non-negotiable for an efficient integration.
- Transparent Pricing: A predictable fee structure without hidden costs is essential for scaling your business effectively.
The Selection Process: How to Choose the Best Payment Gateway
Selecting the right payment gateway is a critical decision that directly impacts your app’s user experience, scalability, and revenue. While industry leaders like Stripe, Braintree (a PayPal service), and Adyen offer robust solutions, the best choice depends on your specific needs. Understanding the nuances of choosing a payment provider involves looking past marketing claims and digging into the factors that matter most: cost, developer experience, and future-readiness.
Cost Analysis: Beyond the Percentage Fee
A gateway’s pricing is more complex than a simple percentage. A comprehensive cost analysis is essential to avoid hidden fees that erode your margins. Scrutinize the entire fee structure, including:
- Per-Transaction Fees: The standard percentage plus a fixed fee (e.g., 2.9% + $0.30).
- Recurring Fees: Fixed monthly charges for using the service or for premium features.
- Incidental Costs: One-time setup fees, international transaction fees, and costly chargeback penalties.
Always check if providers offer volume-based discounts, as this can significantly lower costs as your app scales.
Developer Experience (DX) and Documentation
For your engineering team, the quality of a gateway’s API and documentation is paramount. Clear, comprehensive documentation and high-quality native SDKs for iOS (Swift) and Android (Kotlin/Java) are non-negotiable. They dramatically reduce development time and complexity, which is crucial when learning how to integrate payment gateway in mobile app codebases. A fully-featured sandbox environment for testing is also a must-have, allowing for robust testing without financial risk.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
Your chosen gateway must be a long-term partner, not a short-term fix. Ensure it can handle your projected transaction volume without performance degradation. If your roadmap includes subscriptions or recurring payments, verify that the gateway offers a powerful, easy-to-use billing API. Modern features like built-in fraud detection, advanced analytics, and multi-currency support are indicators of an enterprise-grade platform that can grow with your business.
Navigating these options can be complex. Let our experts help you choose the perfect payment gateway for your app.
The Technical Blueprint: A Step-by-Step Integration Guide
Moving from theory to execution, this section provides a high-level walkthrough of the most secure and efficient method for how to integrate payment gateway in mobile app: the SDK and tokenization approach. This industry-standard process ensures that sensitive cardholder data never touches your servers, dramatically reducing your PCI compliance scope and enhancing security. The flow is split between client-side and server-side responsibilities for a robust and scalable architecture.
Step 1: Setting Up the Client-Side (Mobile App)
Your mobile application is the user’s entry point, but it should never be a vault for sensitive data. The payment gateway’s native SDK is engineered to handle this securely. The process is direct and efficient:
- Install the SDK: Integrate the gateway’s official iOS or Android SDK into your project using standard dependency managers like CocoaPods or Gradle.
- Build the Payment UI: Implement the user interface for collecting payment information. Many SDKs offer pre-built, customizable UI components to accelerate this process and ensure compliance.
- Tokenize Card Details: When the user submits their information, the SDK intercepts it directly, communicates with the gateway’s servers, and converts the raw card data into a secure, single-use token.
- Send Token to Your Server: Your app’s only responsibility is to send this non-sensitive token to your backend for processing. The actual card number never touches your application’s memory post-submission.
Step 2: Building the Server-Side Logic (Your Backend)
Your server acts as the trusted orchestrator. It receives the secure token from the app and communicates with the payment gateway’s API to authorize the transaction. This is where the actual charge is initiated.
Set up your backend with the gateway’s corresponding server-side library (e.g., for Node.js, Python, or PHP). You will then create a secure API endpoint (e.g., /api/create-payment) that accepts the payment token and other transaction details like amount and currency from the mobile app. Using the server-side library and your secret API key, you make a ‘charge’ or ‘payment intent’ API call to the gateway, passing along the token and transaction amount.
Step 3: Handling the Response and Finalizing the Transaction
The final step is a clear, two-way communication loop that confirms the transaction’s outcome for both your system and the end-user. The gateway’s API will respond synchronously with a success or failure status. Your server-side logic must parse this response. On success, you’ll store the non-sensitive transaction details (like a transaction ID, amount, and timestamp) in your database for record-keeping. Finally, your server sends a simplified confirmation back to the mobile app, which then updates the UI to display a “Payment Successful” or “Error” message to the user. This clean separation of concerns is fundamental for building a secure and reliable payment system.
Security and Compliance: Protecting User Data
A successful payment integration is built on a foundation of trust. While the technical steps are critical, ensuring the security of user payment data is paramount. When you learn how to integrate payment gateway in mobile app solutions, you are taking responsibility for sensitive information. Failure to comply with industry standards can result in severe financial penalties, loss of payment processing privileges, and irreversible damage to your brand’s reputation.
The core of payment security revolves around the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), a mandatory set of requirements for any business that handles card data.
Understanding PCI DSS Compliance
PCI DSS is an information security standard designed to reduce credit card fraud by increasing controls around cardholder data. The good news is that modern payment gateways dramatically simplify your compliance burden. By using a gateway’s pre-built UI components (like Stripe Elements or Braintree’s Drop-in UI), sensitive card details are sent directly from the user’s device to the gateway, completely bypassing your servers. This significantly reduces your PCI scope and makes proving compliance via a Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) a much more straightforward process.
Best Practices for Secure Integration
Beyond leveraging your gateway’s tools, implementing a rock-solid security posture is non-negotiable. Adhering to these best practices is a critical part of how to integrate payment gateway in mobile app architecture correctly.
- Always Use Tokenization: Never let raw card data touch your servers. Modern SDKs automatically convert sensitive payment details into a secure, single-use token. Your server uses this token to process the charge, ensuring you never handle or store the actual card number.
- Implement Strong Server-Side Validation: Never trust data sent from the client-side app. Your backend must always validate transaction details, such as the amount and currency, before communicating with the payment gateway API to prevent tampering.
- Enforce Encrypted Connections: All communication between your mobile app, your server, and the payment gateway’s endpoints must be encrypted using up-to-date HTTPS/TLS protocols. There are no exceptions to this rule.
- Regularly Update SDKs: Payment gateway providers frequently update their SDKs to patch security vulnerabilities and add features. Keep your dependencies current to protect your app and users from emerging threats.
Build your app with a team that puts security first. Contact API Pilot.
Finalize Your Integration and Unlock Mobile Commerce
Successfully implementing a payment system is more than just writing code. It’s a strategic process that hinges on meticulous planning, choosing the right gateway, and adhering to strict security standards. Mastering how to integrate payment gateway in mobile app ensures a seamless user experience and builds the trust necessary for your application to thrive. By focusing on a secure, compliant, and user-friendly payment flow from the start, you create a rock-solid foundation for monetization.
While the process is clear, the execution requires precision and expertise. At APIPilot, we specialize in building enterprise-grade payment solutions. Our team has deep expertise in native iOS & Android development, delivering secure, scalable, and PCI-compliant integrations with leading gateways like Stripe and Braintree. We handle the complexity so you can focus on your core product.
Need a robust and secure payment solution for your mobile app? Talk to our experts today!
Build with confidence and power your app’s commercial success.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does it cost to integrate a payment gateway into a mobile app?
The cost involves two primary factors: development hours and transaction fees. A straightforward integration using a robust SDK might take a developer 10-20 hours. For complex, custom-built checkout flows, this can exceed 50 hours. Additionally, gateways charge transaction fees, typically a percentage plus a flat rate (e.g., 2.9% + $0.30), which is an ongoing operational cost. Always factor both initial development and long-term processing fees into your budget.
How long does the payment gateway integration process typically take?
A basic integration using a modern gateway with excellent documentation and SDKs can be completed in a few days. However, a production-ready implementation, which includes building the UI, handling all possible transaction responses, and conducting rigorous security testing, typically takes between one to three weeks. The overall timeline for how to integrate payment gateway in mobile app depends heavily on the complexity of your checkout logic and your team’s experience.
What is the difference between Stripe, PayPal, and Braintree?
Stripe is a developer-first platform known for its powerful, flexible APIs and comprehensive documentation, ideal for custom and complex payment systems. PayPal offers massive brand recognition, providing a fast and trusted checkout experience for millions of global users. Braintree, a PayPal service, acts as a hybrid, offering a strong developer platform that seamlessly incorporates both credit card processing and PayPal payments within a single integration.
Do I need a merchant account to use a payment gateway?
Not always. Modern payment service providers like Stripe and PayPal function as payment aggregators, meaning they process payments for you under their master merchant account. This simplifies setup immensely. In contrast, traditional payment gateways often require you to apply for and maintain your own separate merchant account with an acquiring bank, which is a more complex and time-consuming process.
What is tokenization and why is it important for mobile payments?
Tokenization is a rock-solid security measure that replaces sensitive payment data, like a credit card number, with a unique, non-sensitive string of characters called a “token.” This means your app and servers never handle raw card details, drastically reducing your PCI compliance scope. For mobile apps, this is critical for securely enabling features like one-click payments and subscriptions without storing vulnerable financial information on the device or your infrastructure.
How do I handle recurring payments or subscriptions in my app?
Most enterprise-grade payment gateways offer robust APIs specifically designed for subscription management. You can use their endpoints to create billing plans, manage customer subscriptions, and automate recurring charges. These systems typically also provide webhooks that notify your application of key events, such as successful renewals or failed payments, allowing you to build automated logic to handle these scenarios efficiently.
Can I integrate multiple payment gateways in one app?
Yes, integrating multiple gateways is a common strategy. This approach can improve conversion rates by offering users more payment choices, provide redundancy in case one gateway experiences downtime, and allow for cost optimization by routing transactions through the most economical provider. However, this adds significant complexity to your app’s codebase and requires a more sophisticated logic layer to manage the routing and reconciliation.



